Keeping an eye on your blood sugar levels is a big part of managing your health, especially if you have diabetes. It might seem a bit daunting at first, but learning how to check your blood sugar is actually pretty straightforward. This guide is here to walk you through everything you need to know, from the basic supplies to understanding what those numbers really mean. We'll break down the common ways to test, like the simple finger prick, and touch on newer options too. Let's get you comfortable with checking your blood sugar.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding what your blood sugar numbers mean is key to managing your health effectively.
- You'll need a blood glucose meter, lancets, test strips, and a sharps bin to perform a finger-prick test.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) offer an alternative way to track levels without finger pricks, but they measure fluid, not blood directly.
- Logging your blood sugar readings helps you and your doctor understand patterns and make necessary adjustments to your care plan.
- Tips like warming your hands and using the sides of your fingertips can make the finger-prick testing process more comfortable.
Understanding Your Blood Sugar Numbers
So, you're diving into the world of blood sugar testing, and that's fantastic! It might seem a little daunting at first, but understanding what those numbers mean is a really big step toward feeling your best. Let's break it down.
What Are Blood Sugar Levels?
Basically, your blood sugar level, or blood glucose level, is just a measurement of how much sugar (glucose) is in your blood at any given moment. Glucose is what your body uses for energy, and it comes from the food and drinks you consume. For most people, these levels go up and down naturally throughout the day. But if you have diabetes, these changes can be more significant, and keeping them in a healthy range is super important.
Why It's Important to Check Your Blood Sugar
Checking your blood sugar is like getting a quick snapshot of how your body is doing. It helps you see how different foods, activities, and even stress affect your body. Knowing these patterns allows you to make smarter choices to keep your levels stable. This proactive approach can really help prevent those bigger health issues down the road and helps you manage your diabetes more effectively. It's all about staying informed so you can take charge of your health.
What Do Your Results Mean?
When you get a reading, it's helpful to know what's considered a good range. Generally, for most adults with diabetes, a fasting blood sugar level (that's before you eat) should be between 80–130 mg/dL. A couple of hours after a meal, it's usually good to be under 180 mg/dL. But remember, these are just general guidelines. Your doctor will help you figure out your specific target ranges, which can depend on a lot of things like your age and overall health. It's a good idea to keep a log of your readings to share with your doctor. This way, you can both see trends and make any necessary adjustments to your diabetes care plan.
Don't get discouraged if your numbers aren't perfect every time. Think of each reading as a piece of information that helps you learn more about your body. It's a journey, and every bit of knowledge is a win!
Gathering Your Blood Sugar Testing Supplies
Getting ready to check your blood sugar is pretty straightforward, and having the right gear makes all the difference. Think of it like getting your tools together before starting a fun project – you want everything to be easy to find and ready to go.
Choosing The Right Blood Glucose Meter
There are tons of glucose meters out there now, and picking one can feel a bit overwhelming. Your best bet is to chat with your doctor or diabetes educator. They can help you find a meter that fits your needs, especially if you have vision issues or other specific requirements. Some meters might even be available through programs that help cover costs, like the Assistive Devices Program if you have diabetes. It's worth asking about what options are available to you.
Understanding Finger Prick Devices and Lancets
These are the little gadgets that help you get that tiny drop of blood. The device holds a lancet, which is the tiny needle that does the pricking. You can usually adjust how deep the lancet goes, which is handy for different skin thicknesses. Lancets come in different sizes too; thinner ones (higher gauge) are often less painful but might not always give you enough blood. Remember, you can only use a lancet once, so always pop in a fresh one for each test.
Test Strips: What You Need to Know
Test strips are what your meter uses to actually read your blood sugar. They usually come in a bottle or box, and you need to make sure they're the right kind for your specific meter. Always check the expiration date on the test strip container – using expired strips can give you inaccurate readings. It's also important to store them properly, usually in their original container, away from heat and moisture. If you're ever unsure about where to get your strips or if they're the right ones, your healthcare team is the best resource.
Keeping your supplies organized and knowing how to use them properly will make your blood sugar testing routine much smoother. Don't hesitate to ask your healthcare provider for a demonstration if you're not feeling confident with any part of the process.
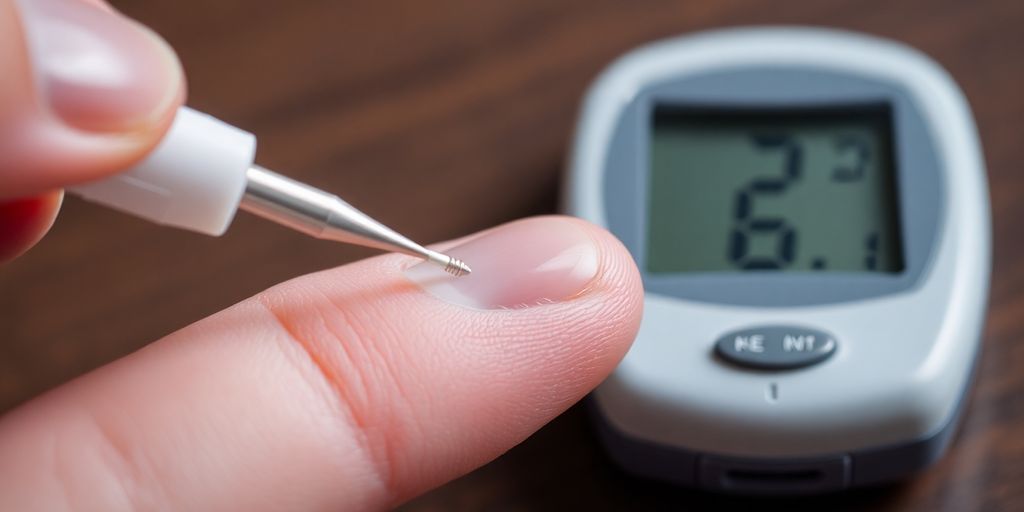
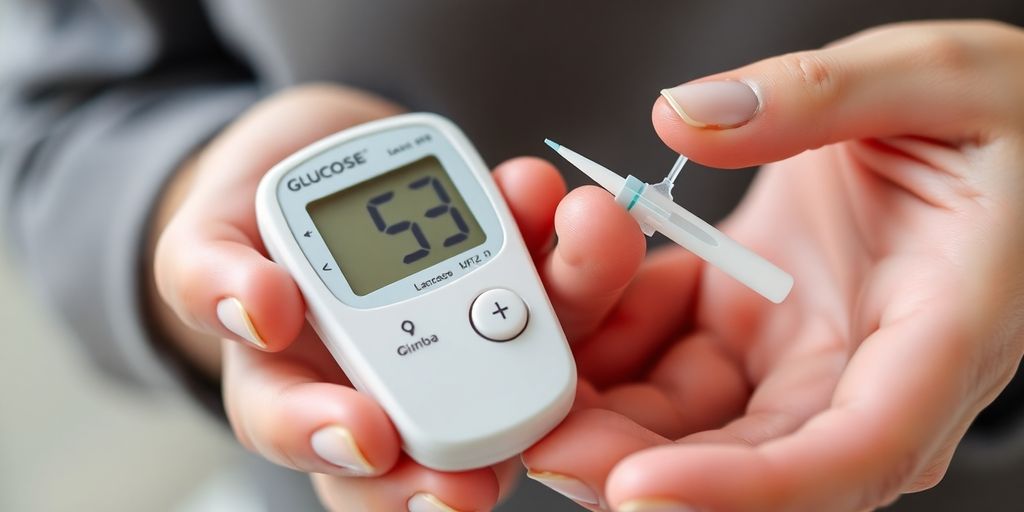
Mastering The Finger-Prick Test
Alright, let's get down to the nitty-gritty of the finger-prick test. It might sound a little daunting at first, but honestly, it's pretty straightforward once you get the hang of it. Think of it as a quick snapshot of what's happening with your blood sugar right at that moment. It's a really useful tool to help you understand how different foods, activities, or even stress levels might be affecting you.
Preparing For Your Test
First things first, cleanliness is key! You'll want to wash your hands with warm, soapy water. Make sure they're completely dry afterward. Avoid using hand sanitizers or lotions right before, as the ingredients in them can sometimes mess with your reading. It's also a good idea to have everything you need laid out: your meter, a fresh lancet, and a test strip. Getting a new lancet ready is important because blunt lancets can be more painful.
Getting A Blood Sample
Now for the actual prick. Grab your lancing device, which you've already loaded with a fresh lancet. Gently press the device against the side of your fingertip. You'll feel a tiny pinch – that's it! The side of your fingertip is usually best because it's less sensitive than the pad. You don't need a huge drop of blood, just a small one. If you don't get enough the first time, don't worry, just try squeezing your finger a little more gently. You can also try washing your hands with warm water beforehand to help with blood flow. Remember to use a different finger each time you test, and try to avoid the very tip of your finger if possible.
It's totally normal to feel a bit anxious about this part, especially at the beginning. Many people find that the more they do it, the less it bothers them. Plus, modern lancing devices are designed to be as gentle as possible.
Reading Your Results
Once you have a nice little blood drop, carefully touch the edge of the test strip (which should already be in your meter) to the drop. The meter will usually draw the blood into the strip automatically. Then, just wait a few seconds for the number to pop up on the meter's screen. This number is your blood sugar reading. It's a good idea to jot this down in a logbook or on your phone right away, along with any notes about what you ate or did that day. This helps you see patterns over time. If you're ever unsure about what the number means, don't hesitate to ask your healthcare provider. They can help you understand your personal target ranges.
Exploring Continuous Glucose Monitors
How CGMs Work
So, you've probably heard about Continuous Glucose Monitors, or CGMs. They're pretty neat! Instead of just a quick snapshot like a finger prick, a CGM uses a tiny sensor that you wear under your skin, usually on your arm. This sensor measures the glucose in the fluid between your cells, called interstitial fluid, all day and all night. Your glucose levels are then sent wirelessly to a reader or even your smartphone. This gives you a much more complete picture of your glucose trends. It's like having a personal glucose detective working 24/7!
CGMs vs. Finger-Prick Tests
Think of finger pricks as a single photo, and a CGM as a whole movie. Finger pricks tell you your glucose level right now. CGMs, on the other hand, show you where your glucose has been and where it's heading. This means you can see if your levels are rising or falling quickly, which is super helpful. While CGMs are awesome for tracking trends, it's good to know they measure glucose in the fluid around your cells, not directly in your blood. This can mean a slight delay, sometimes up to 15 minutes, between your blood glucose and the CGM reading, especially after eating or exercising. That's why sometimes your doctor might still want you to do a finger prick to confirm a reading. You can find out more about CGM technology.
When to Talk to Your Doctor About CGMs
If you're curious about CGMs, the best first step is always to chat with your doctor or diabetes care team. They can help you figure out if a CGM is a good fit for your specific needs and diabetes management plan. They'll also guide you on how to use one effectively and what to do with all that new information. It's all about finding the tools that work best for you on your health journey!
Keeping Track of Your Progress
Keeping a good record of your blood sugar readings is super helpful. It's like having a personal diary for your body's responses to food, activity, and medication. This information is gold for you and your doctor.
The Importance of Logging Your Readings
Think of your logbook as your personal health detective kit. Each number tells a story about what's happening inside you. Tracking your levels helps you and your healthcare team see patterns and figure out what works best for managing your diabetes. It's not about judgment; it's about information. This data helps make smart adjustments to your meal plans, exercise routines, or medication, all aimed at keeping you feeling your best.
Using Your Logbook Effectively
So, how do you make the most of your logbook? Here are a few pointers:
- Be Consistent: Try to record your readings around the same times each day, especially before and after meals, and before bed. This gives a clearer picture.
- Note Down Everything: Jot down not just the number, but also what you ate, if you exercised, and how you were feeling. Little details can make a big difference.
- Keep it Accessible: Whether it's a physical notebook or an app, make sure it's easy to carry and update. Some people even use special apps that can sync with their glucose meters.
Keeping track helps you understand how your body reacts to different things. It's a way to be proactive about your health and make informed decisions. Don't get discouraged by numbers that seem off; just see them as clues to help you improve.
Understanding Your Target Ranges
Your doctor or diabetes educator will help you figure out what your target blood sugar ranges should be. These are the numbers you aim for. They can vary depending on the time of day and whether you've eaten. Knowing these targets gives you something to work towards and helps you see if your current plan is hitting the mark. It's all about finding that sweet spot for your health. You can find tools to help you monitor your daily wellness, including glucose levels, all in one place on this platform.
Tips for a Smoother Testing Experience
Sometimes, checking your blood sugar can feel like a chore, but it doesn't have to be a hassle! With a few simple tricks, you can make the whole process much easier and even less painful. It’s all about finding what works best for you.
Making Finger-Pricking Less Painful
Nobody enjoys a poke, right? To make it hurt less, try warming your hands first. You can do this by running them under warm water or just holding them in your pockets for a bit. Also, don't prick the very tip of your finger; the sides are usually less sensitive. And remember, lancets get dull with use, so using a fresh one each time is key. You can also adjust the depth setting on your lancing device – start shallow and increase if needed. A thinner lancet (higher gauge) often means less discomfort.
Choosing the Best Spot for Your Test
Your fingers have lots of nerve endings, which is why they're sensitive. While fingers are common, you can actually test on other parts of your body too, like your palm or forearm, if your meter allows it. These areas might have fewer nerve endings. If you stick to your fingers, try to rotate which finger you use and which part of the finger you prick. Avoid the very center and areas close to your nails. It’s a good idea to get advice from your healthcare team on the best spots for you.
Safe Disposal of Used Lancets
This is super important for safety! Once you're done, never just toss a used lancet in the regular trash. They're sharp and can accidentally prick someone else. The best way to handle them is to put them in a special sharps container. If you don't have one, a sturdy plastic container with a secure lid, like an empty laundry detergent bottle, can work in a pinch. Just make sure it's clearly labeled. When it's about three-quarters full, you'll need to dispose of it properly according to your local guidelines. Your doctor or pharmacist can tell you how to do this safely. Keeping your blood sugar in check is easier when you know how to manage your supplies correctly.
You've Got This!
So, checking your blood sugar might seem like a lot at first, but you'll get the hang of it. It's really just about getting to know your body a little better. Think of it as a tool to help you stay on track and feel your best. Keep up the great work, and remember, you're not alone in this. There are tons of resources and people ready to help if you ever have questions. You're doing a fantastic job taking charge of your health!
Frequently Asked Questions
What exactly is blood sugar and why should I care about it?
Checking your blood sugar, also called blood glucose, tells you how much sugar is in your blood at any moment. This is super important because sugar is what your body uses for energy. Keeping your sugar levels in a good range helps your brain, heart, and kidneys work well. If your sugar is too high or too low too often, it can cause health problems down the road.
How do I actually check my blood sugar at home?
You can check your blood sugar using a small gadget called a blood glucose meter. It works by you poking your finger with a tiny needle (called a lancet) to get a drop of blood. You then put that drop on a special strip that goes into the meter. The meter reads the strip and tells you your sugar number. Some people also use a Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM), which is a sensor you wear that checks your sugar in the fluid around your cells.
How do I choose the right blood sugar testing meter?
It's best to talk to your doctor or a diabetes educator about which meter is right for you. They can help you pick one that's easy to use and fits your needs. They can also tell you if you can get one through your insurance or if you'll need to buy it yourself. Don't forget to ask about the test strips too, as they need to work with your specific meter.
Where is the best place to prick my finger to get blood?
Most people check their blood sugar on the sides of their fingertips, as this area has fewer nerves. It's a good idea to switch fingers each time and to prick the side of the finger, not the fleshy pad. Some meters also let you test on your forearm or thigh, but it's best to check your meter's manual or ask your doctor if this is an option for you.
Why is it important to write down my blood sugar readings?
Keeping a record of your blood sugar readings is really helpful! You can write them down in a notebook, a special logbook, or even use an app on your phone. This helps you and your doctor see how different things like food, exercise, or stress affect your sugar levels. It's like a diary for your body's sugar, showing patterns over time.
Can I really do this myself, or do I need a doctor every time?
Yes, you can! Your doctor or a diabetes educator will show you how to do it safely and correctly. They'll explain how to use the meter, the lancet device, and what to do with the used lancets (you should throw them in a special sharps container). It might feel a little strange at first, but it gets easier with practice.